GraphicAnalysis: Spring Festival consumption to boom amid historical high travel rush
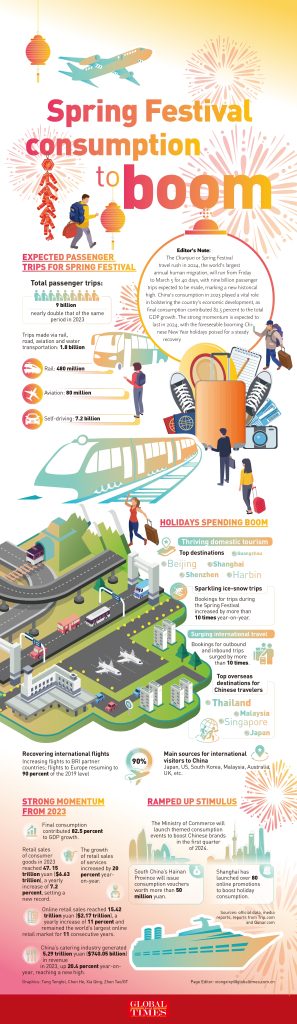
Spring Festival consumption to boom amid historical high travel rush GraphicAnalysis: GT

Spring Festival consumption to boom amid historical high travel rush GraphicAnalysis: GT

While electricity trade between India and Nepal appears to give the former a commanding advantage against China in Nepal's hydropower sector, there is also growing concern as to whether India's geopolitical game of edging China out could jeopardize Nepal's power projects and energy supply ambitions.
Due to a strategic policy change that India implemented in 2018, India has outpaced China in securing hydropower contracts in Nepal, BNN Breaking reported on Monday.
Media attention to the competition for influence in Nepal's hydropower sector came a few days after Nepal and India reportedly signed a power trade agreement for Kathmandu to export 10,000 megawatts of hydroelectricity to India over the next 10 years, according to Reuters.
Since the hydropower sector in the Himalayan nation has been considered a crucial arena for geopolitical tussles between India and China, the development was touted by some Indian and Western media outlets as evidence of India's growing influence in the region.
Objectively speaking, it is a welcome development that India and Nepal are moving toward strengthening their power trade, which is in the interests of both sides, but that doesn't necessarily mean that Nepal's development should fall victim to India's geopolitical maneuvers.
Indeed, India's power trade policy, which prohibits the purchase of electricity produced by projects invested by Chinese companies, has cast a shadow on the investment dynamics of Nepal's energy infrastructure.
In 2018, India changed its electricity buying policy to prevent the purchase of power produced via the investment of nations with which it does not have a "bilateral agreement on power sector cooperation." Although it didn't explicitly mention China, hydropower produced by Chinese-funded or Chinese-built plants is actually excluded in power trade with Nepal. As a result, Nepal has removed Chinese developers from six hydropower projects and given four hydro contracts to Indian companies, Reuters reported in May 2023, citing an industrial official in Nepal.
Indian companies have contracts to build and operate 10 hydropower plants in Nepal, while Chinese developers have such contracts for five of them, according to media reports.
The reason why India's power purchase policy can have such great influence on Nepal is because its power supply has undergone dramatic changes over the past decade, and its generation capacity is now enough to meet domestic needs.
This also means that Nepal needs to find overseas markets for its surplus electricity during the rainy season, with India and Bangladesh being the target markets. Because of its geographical location, even the power trade between Nepal and Bangladesh requires India's participation.
But such trade needs should not be tools used to exclude other participants for geopolitical interests. It is nothing but narrow-minded for a regional power to be obsessed about the geopolitical significance of its neighbors while neglecting their development needs.
This approach won't gain positive regional influence for India. Specifically, given the past and current situation of Indian companies' hydropower projects in Nepal, it is questionable whether India has the ability to support Nepal's hydroelectric development, which reportedly has the potential to produce 72,000 megawatts of hydroelectricity.
By comparison, Chinese companies' contributions to Nepal's hydropower development are evident. With the participation and support of Chinese companies, Nepal has turned into a net exporter of electricity.
China has not only invested in hydropower projects in Nepal, but it has also discussed a cross-border transmission line with Nepal, which may be a solution to Nepal's export needs.
Still, it is our sincere hope that India can have a more open-minded attitude toward Chinese investment in Nepal. If geopolitics is set aside, it will find that there is cooperation space between China and India on this issue, which is beneficial for all parties in the region.
China has construction and technological advantages in hydropower projects, and Nepal's hydropower development, if smooth, will benefit India and Bangladesh.
In addition to hydropower projects, China and Nepal also have cooperation involving other infrastructure projects, which are also beneficial for regional development, such as the China-Nepal railway that is intended to greatly improve connectivity in South Asia. It would be a pity if India only saw these developments as part of its geopolitical competition with China.
If India is really concerned about its influence in the region, it is advised to invest more and help Nepal and other regional countries with infrastructure development, promoting regional economic prosperity.
The development of South Asia now hinges to a large extent on whether India can adopt a cooperative attitude in the face of the regional needs. This is also the common wish of many countries in the region.

China's Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) has approved graphite export applications from multiple entities, a ministry spokesperson said on Thursday, reiterating that its export control mechanism is not a ban.
Exercising exports control measures on certain graphite products is of common international practice and the China's export control rules are aimed at fulfilling international non-proliferation obligations and safeguarding China's national security and interests, ministry spokesperson He Yadong told a press briefing on Thursday.
He made the remarks in response to reports that some Chinese graphite exporters are cleared to export their products to major South Korean battery companies.
China in October announced plans to optimize export controls on some categories of graphite, a key material in making electric vehicle battery, with new rules taking effect on December 1. The export of artificial graphite materials and related products with high purity, high strength and high density, as well as natural flake graphite and associated products, are subject to the new rules.
Due to China's critical role in the global graphite supply chain, the export control measures received immediate attention abroad.
He emphasized that China's export control measures should not been seen as outright export ban and the ministry has approved a number of graphite export applications that that comply with relevant regulations.
The ministry will continue to review other license applications and make decisions in accordance with legal procedures, He said.
Experts said China's export control rules on certain graphite items are restrained and professional and are in line with international practice.
Earlier, the ministry said that China remains committed to maintaining the security and stability of the global industrial and supply chains.

A white paper released by the Japanese Chamber of Commerce and Industry in China on Monday showed that more than half of Japanese companies increased or maintained investment in China last year, underlying the resilience of the Chinese market.
Experts said Tokyo's move of following the US to seek "decoupling" with China in some fields have affected Japanese companies' investment in China, calling for the Japanese side to rule out external disturbance and pursue new cooperation areas with China for win-win results.
Conducted between November 23 and December 13, 2023, the survey collected responses from over 1,700 Japanese companies doing business across China. It covered a wide range of industries from electronic machinery to chemicals, food and medicine, according to a report sent to the Global Times on Monday.
About 38 percent of Japanese companies said that they maintained the same investment level last year as 2022, while another 15 percent said they "significantly increased" or "increased" their investment in China.
Reasons given for increased investment include business expansion in the wake of the COVID-19, conforming to the electrification and intelligence of the automotive industry, and increasing efficiency and functionality through automation.
Around 54 percent of the companies surveyed said they are satisfied with the business climate in China, up 3 percentage points compared with the chamber's last survey, it said.
Those surveyed said their businesses in China is relatively "grim," but slight improvement is also being made, it said, stressing that 51 percent of Japanese companies considers Chinese market their "most important market" or "one of the three most important markets."
"The result of the survey revealed the contradiction state of mindset of Japanese companies. Japan's China policy has shown tendency of following the US in recent years, and the Japanese side's 'industrial decoupling' from China have affected some Japanese companies' investment and operations in China," Xiang Haoyu, a research fellow at the China Institute of International Studies, told the Global Times on Monday.
Despite geopolitical volatility, about half of Japanese companies are willing to maintain or increase their investment in China, which underscores the resilience and potential of the vast Chinese market, Xiang said.
Looking ahead to 2024, Xiang is cautiously optimistic about China-Japan economic and trade relations. Customs data showed that Japan is still a major trade partner of China and the complementary nature of the two economies persist, but the Japanese side ought to rule out external meddling to explore new cooperation areas with China for greater win-win results, he said.
According to data released by the General Administration of China, the volume of bilateral trade between China and Japan dropped 10.7 percent year-on-year to reach $318 billion in 2023.
Japan announced in March 2023 a draft revision to a ministry ordinance on its Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Act, adding 23 chip-manufacturing items that require government approval for export, which includes equipment for cleaning, checkups and lithography, a technology essential in producing cutting-edge chips. It took effect in July.

Generative artificial intelligence (AI) can complete image creation and document writing in seconds, bringing novelty but also causing more anxiety for creators.
The first case of copyright infringement involving AI-generated images in China has recently been finalized, with the plaintiff Li Yunkai winning the lawsuit but waiving the 500 yuan ($70) compensation from the defendant.
Li Yunkai recently told the media that the compensation is not important to him; he rather hopes that the court can provide a clear criterion on whether using AI to generate images constitutes original work and possesses original work of authorship.
In this particular case, the Beijing Internet Court recognized the picture generated via text-to-image AI image generator should be considered original “artwork” under the protection of copyright laws based on the “originality” and intellectual input of its human creator.
However, industry observers noted that the case also emphasized whether the artificial intelligence-generated content (AIGC) constitutes a work with copyright cannot be generalized but should be decided on a case-to-case basis.
Why is that? Observers argued that, to protect AIGC, it is necessary to establish whether the subject of the right is a human being rather than the machine or the AI.
Li Zonghui, the vice president of the Institute of Cyber and Artificial Intelligence Rule of Law affiliated with Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, told the Global Times that the current copyright law defines the subject of the work as the author, citizens, legal persons, and social organizations. It is evident that AI does not meet this requirement.
Back in 2018, the US Copyright Office received its first known copyright registration application for an AI-generated work. But later in 2023, the court rejected the application because AI, as a non-human, is not subject to copyright protections.
In this case, Stephen L. Thaler intended to claim authorship of a visual image titled “A Recent Entrance to Paradise,” which was generated by his developed AI system known as the "Creativity Machine."
“Protecting content generated by non-human beings as works with copyright is fundamentally contrary to the legislative purpose of copyright law,” Li Zonghui noted. In the Beijing case, the court rule was based on the fundamental principle of protecting the rights of “human being.”
According to the court, if an AI-generated image reflects the original intellectual investment of a human being, it should be considered artwork and protected under copyright law. However, determining the extent of the original intellectual investment made by a human being in the creation process poses a challenge.
The Beijing Internet Court believes that the plaintiff Li Yunkai designed the visual elements of the character and its presentation through prompts and set parameters for the layout and composition of the image. He continued to add prompts and modify parameters after obtaining the first image, constantly adjusting and revising, and finally obtained the image. The process reflects the plaintiff's aesthetic choices and personal judgment, the court believed.
Li Zonghui pointed out that if a work is purely generated by AI without any contribution from the user, it may not be subject to copyright infringement. The key factor lies in the prompts and what kind of modify parameters given to the machine and whether they constitute originality.
Some industry observers argue that writing prompts to generate a work is a simple task, resulting in a minimal intellectual contribution to AI-generated image creation.
AI systems have the capability to replicate on a large scale, enabling the generation of a vast number of images or content within a short period. If copyright protection is granted to all of this, it will not foster innovation for society as a whole, stated You Yunting, a Shanghai-based lawyer, in an interview with The Paper.
Machines’ deep learning is essentially a statistical process that involves collecting large-scale data and performing rapid calculations and deductions. Therefore, it is not the same concept as human original expression, Andy Sun Yuanzhao, executive director at The Asia Pacific Legal Institute, wrote on Copyright Theory and Practice recently.
Apart from lawsuits relating to AI-generated images, China has also seen a first legal dispute over a virtual human.
In July 2022, a technology company in Hangzhou uploaded a video to their Douyin account featuring Ada, a virtual human created by Shanghai-based Xmov Technology but failed to acknowledge Xmov as the original creators. The Hangzhou Internet Court later sided with Xmov, ordering the infringing company to pay 120,000 yuan in compensation.
Analysts said there is a connection between virtual humans and works in copyright law and the right of portrait and personality in civil law.
If the character’s appearance is completely newly designed, then the virtual digital human may constitute an artistic work and be protected by copyright law. If the character is based on the modeling of a specific natural person, then the virtual digital human involves the use of the likeness of a real person and requires the permission of the right of personality holder, Li Zonghui told the Global Times.
One judgment of copyright infringement will certainly lead to more subsequent lawsuits. The aftereffects will be the increase cost and market entry barriers for the subsequent development of the AI industry, Sun said.
Given that these lawsuits usually last for a long time, unless the parties can reach a pre-litigation settlement, the entire AI industry is likely to be in a state of uncertainty for a considerable period of time in the future, Sun said.
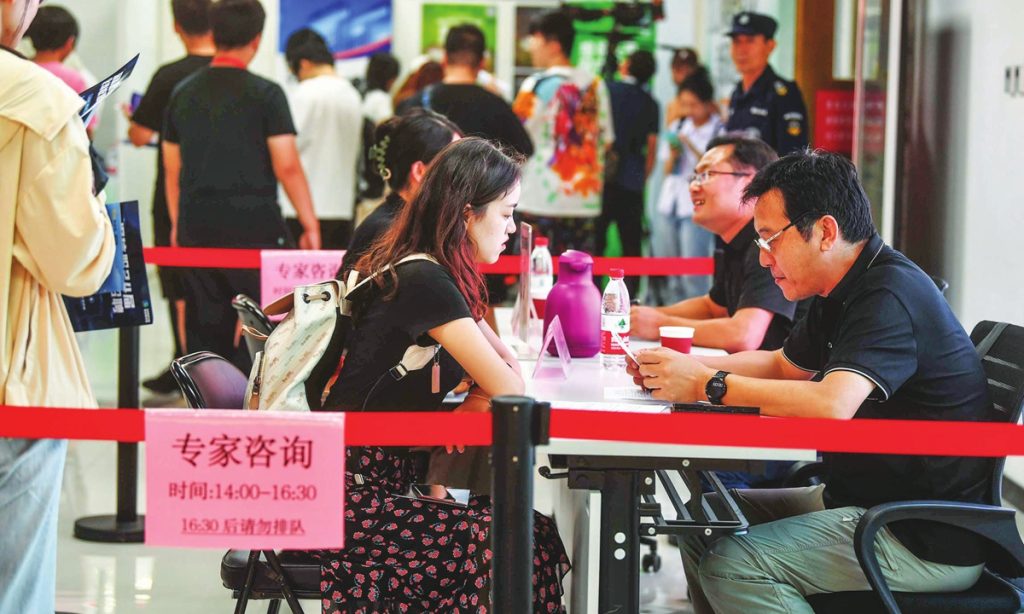

In a bid to enhance services for flexible workers, China's Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security (MHRSS) issued a comprehensive set of guidelines aimed at standardizing flexible job markets on Monday, aiming to provide workers with transparent and regulated services. The notice is in line with its commitment to integrate this sector into the broader employment public service system.
In the notice, the MHRSS outlined several key areas related to flexible job markets that require attention and improvement.
China has a vast population of flexibly employed individuals, and the rapid development of the internet industry has sparked changes in the job market, making it easier for young people to find such jobs, but the market remains largely unregulated, Tian Yun, a veteran economist based in Beijing, told the Global Times on Monday.
The notice emphasized the need to clearly define the service orientation of flexible job markets. The markets, which often operate outside the public service sector, will now be brought under the umbrella of the public employment service system, providing accessible, flexible and inclusive labor services.
The ministry also said it aims to improve services in the markets, stressing the importance of providing comprehensive services such as job matching, career guidance, and skills training, which is particularly significant in light of China's rapidly evolving job market, where new sectors and opportunities are constantly emerging.
The notice also highlighted the opening and operation of flexible job markets, and called for building service stations and recruiting sites that meet local workers' conditions and demands. It also clarified the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders in managing and overseeing the markets.
Data analysis is an important part of the notice, as job markets will be asked to publish key indicators, such as the ratio of job seekers to available positions. The information is critical for job seekers and employers in making decisions.
Standardizing service requirements is another part of the notice. The MHRSS has asked local departments to standardize naming rules for local job markets, to unify business processes and service standards, and implement clear regulations to ensure transparency in services. The ministry will soon publish a unified national logo for the markets across the country.
The notice also underscored the importance of capacity building within the sector, which includes measures such as enhancing staff training and expanding the workforce through multiple channels to cater to the growing demands of this dynamic market.
Many flexible workers lack adequate protection for their labor rights. The notice from the MHRSS provides directional guidance for developing the flexible job markets, but concrete implementation by local authorities is needed to ensure compliance. Regulating flexible employment requires a concerted effort from the relevant authorities, as well as support and cooperation from society, Tian said.
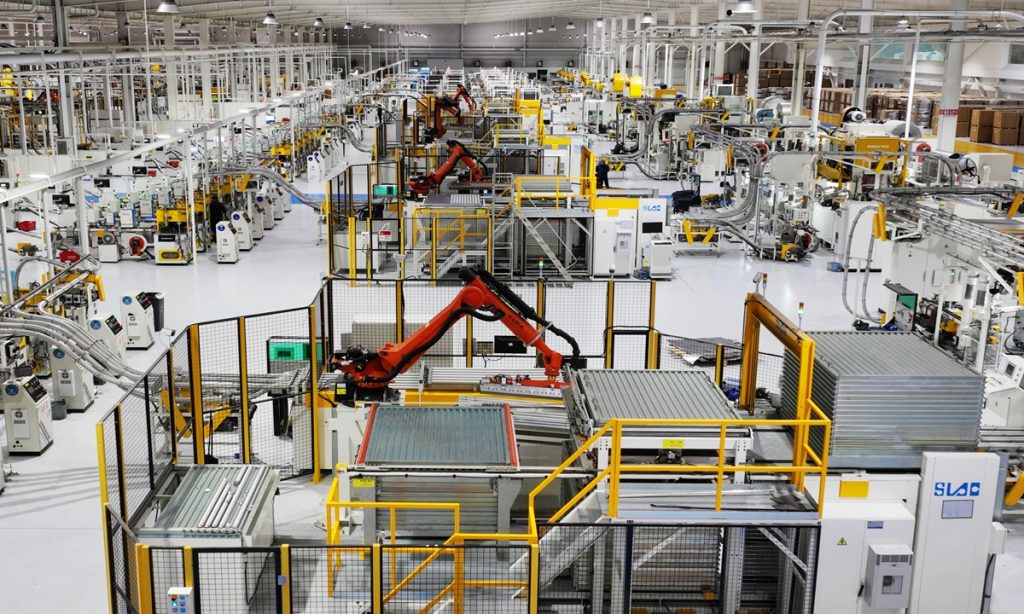

Last year, Chinese enterprises including major technology brands expanded their footprint on the global market. It was also the first year for upgraded versions of "Made in China" to compete in the markets of the developed economies in all aspects.
In 2023, China's foreign trade and investment rose steadily, with a trade surplus of more than $730 billion in the first 11 months. China was the only major economy with an inflation rate lower than the central bank's 2-percent target.
In retrospect, in the fields of semiconductors, artificial intelligence, new-energy vehicles or batteries, the technological value of Chinese manufacturing was increasingly recognized globally. In the second half of the year, many Silicon Valley entrepreneurs chose to return to China, seeking cooperation with the world's largest factory, known for its high manufacturing efficiency and growing competitiveness.
In 2024, the globalization of the high-tech sector will be irreversible, and Chinese high-tech companies will continue to "go global." There will be more and more Chinese companies setting up factories in both the developed and developing economies, and concurrently, there will also be an increasing number of young Chinese entrepreneurs appearing on the international business stage.
The rapid development of the Chinese economy over the past 45 years can be attributed to the reform and opening-up policy. Maintaining a competitive advantage in the global manufacturing industry is crucial for China's industrial transformation and upgrading of the economy, as well as ensuring the stability of the yuan's exchange rate and the well-being of the public in the face of global challenges.
The development of Chinese economy demonstrates that China's goal is not to "dominate the world", but to share the dividends of its development. This explains why China's foreign policies won't follow the heels of the traditional colonial powers by bullying the weak and poor, and China's contributions have been widely recognized by countries and regions participating in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Under the long-term goal of maintaining steady and sustainable development, the Chinese economy saw a robust recovery in 2023. In addition to effectively controlling inflation, various indicators such as electricity generation, transportation of goods and passengers and retail sales all exhibited a gradual recovery, surpassing market expectations.
The improved economic data can be attributed to the continuous implementation of policies such as poverty alleviation, the BRI and the development of high-end manufacturing. They also stem from the continuous improvement in the capital intensity of modern agriculture and manufacturing, offsetting insufficient growth momentum caused by a slowdown in the real estate sector.
Investors' expectations for the economy's future are diverging. There is a common saying in the international investment community: "optimists tend to be successful and pessimists tend to be right." China's market size and development potential are enormous, and only optimistic entrepreneurs who keep up with the times can get their due rewards.
The main battlefield of competition for Chinese companies has long expanded from first- and second-tier Chinese cities to county towns, which benefits more Chinese consumers, as brands and consumption patterns that used to only exist in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen are increasingly entering local towns and rural areas.
The upgrading of the financial industry will also be an important aspect of the Chinese economy in 2024. Commercial banks such as China Agricultural Bank, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China and China Construction Bank have all lowered their deposit interest rates, which for the first time are below the benchmark interest rate set by the People's Bank of China.
This is a new milestone in Chinese financial history. It signifies that China has transitioned from a period of relying on foreign investment during the early stages of reform and opening-up to a new stage where domestic capital is abundant.
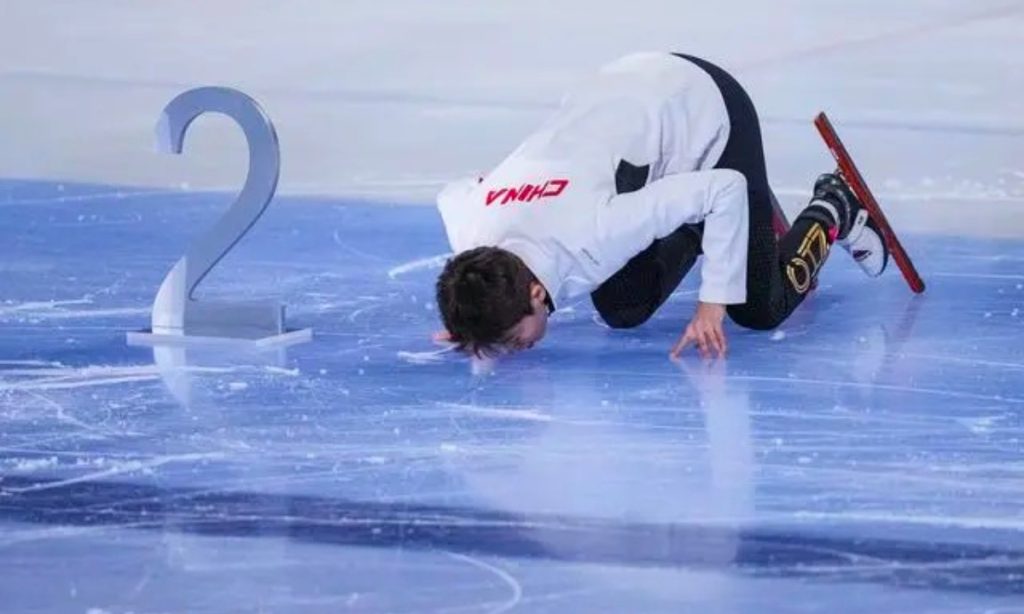

China's veteran short track speed skater Fan Kexin kissed the ice surface at the Capital Indoor Stadium again on December 9 at the ISU Short Track World Cup in Beijing, as she returned to competition after a nearly two-year hiatus after the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics.
Fan, who is among China's squad that won a gold medal in the 2,000-meter mixed relay at the home Olympics, finished her events on Saturday with two silver medals.
Fan clocked the women's 500 meters with 43.117 seconds, followed by her younger teammate Wang Ye with 43.176 seconds. At the awarding ceremony for the race, Fans kissed the ice surface again.
"I just love this ice so much," Fan, a three-time Olympian, told reporters after Saturday's races at the ISU short track World Cup event in Beijing. "As long as I have chances to compete, I will do my best."
Fan noted that now she is enjoying skating, thanks to the overwhelming support from Chinese fans.
"Their support means a lot to us. Now we are receiving massive attention from the fans compared to the past, which also boosted our confidence and performances," the 30-year-old said.
Fan's kiss on the ice surface at the Olympics was remembered as one of the emotional moments at the quadrennial event by Chinese short track fans.
Speculation was rampant that the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics would be Fan's swansong, as she had not participated in any competition since.
Her return has been considered a boost for the Chinese women's short track team, which is currently in a rebuilding phase as it aims to return to the sport's top-tier.
Along with her younger teammates, Fan is also among the team that won a silver medal in the 2,000-meter mixed relay at the World Cup event. Her younger teammate Wang, who is just 18, has welcomed her return, crediting Fan who "strengthened" the whole team's confidence with competing.
Speaking about the winning inheritance of the short track team, which is the most successful Chinese winter sports team, Fan said it is not just "talk the talk."
"The inheritance is in their hearts to take on the task and responsibility to grow, rather than just talking out loud about inheritance," Fan said.
"It feels great to compete with my young teammates side by side. I hope these young athletes could participate in the World Cup, World Championships, the Olympics step by step and achieve better results."
Short track competitions are currently the most popular winter sports races in China, as the stadium hosting Chinese athletes often has near-capacity attendance drawn by the chance to witness the star-studded national squad.
Saturday's race saw Team China bag four silver and one bronze medals. The competitions will continue on Sunday, including a highly-anticipated men's 5,000-meter relay final.

China saw more than 40,200 deceased organ donations from 2015 to the end of 2022, with 120,100 major organs donated. Additionally, more than 6.55 million people have voluntarily registered for organ donations, according to the China Organ Transplant Development Foundation (COTDF).
The COTDF revealed the figure at the 7th China-International Organ Donation Conference and the Belt & Road Symposium on Organ Donation and Transplantation International Cooperation Development, which kicked off in Nanning, South China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, on Saturday.
Currently, China ranks second in the world and first in Asia in terms of the number of organ donations, benefiting numerous patients in need. The COTDF said that 5,628 deceased organ donations were made in 2022, an increase of 6.75 percent compared to 2021.
More than 20,000 organ donations are made in Chinese mainland each year, ranking second in the world in terms of data. However, organ donors per million people (PMP) is less than 4 percent, which is far from satisfactory compared to the 47 percent in developed countries, Huang Jiefu, chairman of China Human Organ Donation and Transplantation Committee and chair of the COTDF Advisory Board, told the Global Times on Saturday.
He pointed out that there are not enough hospitals in China to satisfy patients' demand for organ transplants. "China currently has only slightly more than 70 hospitals that perform heart and lung transplants. Thus, there is still a shortage of doctors and hospitals to meet the needs of the people," said Huang.
In October, China's State Council held an executive meeting that adopted a draft revision to the regulations on donation and transplantation of human organs.
The government aims to establish a system for tracing and supervising the whole procedure of donating and transplanting human organs. It will enhance ethical reviews on how human organs are obtained and crack down on crimes involving human organs, according to the meeting.
Talking about the revision, Huang used the phrase "scraping poison off the bone" to describe the determination in China's organ donation reform.
He said that under the leadership of the central government, this reform has achieved significant victories and has been widely recognized by the international community. The revision of the regulation demonstrates the Party and the country's emphasis on organ donation, providing strong legal protection for the high-quality development of the organ donation cause, said Huang.
Huang said that the word "donation" carries special meaning. With the coming of the regulation, organ donations will be more transparent, and it also calls for more people to get involved in organ donations and transplants. In the future, it is hoped that China's organ transplantation technology will spread to more countries in the Belt and Road Initiative via the Organ Donation and Transplant under the Framework of the Belt and Road Initiative, said Huang.
Talking about China's recent achievements in organ transplantation, John Fung, president-elect of the Transplantation Society, told the Global Times that in terms of survival, China meets international standards.
"The primary accomplishment of China's transplant efforts is that a country that had very limited transplants 30 years ago is now able to compete with any other transplant program in the world in terms of quality," said Fung.
However, Fung also mentioned that the primary challenge in China is that "it has a very large population and still not enough access to transplants. There are many barriers to transplants for the common people in terms of costs as well as a shortage of organs."
Yet he said that China is getting there as the trajectory of donations in the country is increasing fast, thus he is confident that five years from now China will move to a much higher rate of donation.
The Belt & Road Symposium on Organ Donation and Transplantation International Cooperation Development held a launch ceremony, during which those in attendance agreed to establish a series of action plans in the areas of leadership, management, quality control and technological innovation in organ donations and transplantations based on the principles outlined by WHO Guiding Principles on Human Cell, Tissue and Organ Transplantation.
Through continuous strengthening of interaction, deepening of mutual trust, and fostering of friendship, the goal of self-sufficiency in organ donation will be achieved.
Fung also mentioned that there is an organized conspiracy on the international stage that tries to play down the accomplishments of China's organ donation experience, by feeding misinformation about transplants in China to further damage the country's reputation.
For example, a new wave of accusations of "organ harvesting" in China has emerged. Following some Western media reports from the China Tribunal, which accused the Chinese government of "harvesting organs from Falun Gong practitioners" and Uygurs "detained in camps" since June 2019, VICE magazine's France version also released a new report on the same topic on June 19, offering more so-called "evidence."
By digging into those stories, the Global Times has found out that such claims are lies interwoven by members of the Falun Gong cult, separatists from Xinjiang and overseas anti-China forces with the purpose to further paint China as a devil mistreating minorities in Xinjiang, to smear the country's organ transplantation and donation system and its anti-terrorism work in Xinjiang, and to instigate the international community to further pressure China.
In response to this recent slander, Huang said that China's reform on organ transplantation is to keep friends close and keep enemies closer. "You can never wake up someone who is pretending to be asleep… we are not afraid of those slanders, as long as what we are doing is justified and is on the right course."
Fung suggested that more publications about "China's organ transplantation be disseminated globally for people to understand that China complies with international standards and that their outcomes for transplantations are as good as anybody else's. As transplantation society president I will do my best to make it more open for the world to understand and appreciate w